To provide better Customer Service bank and financial institutions must evolve continuously and be in competitive in the saturated financial sector. With evolve of virtual banking solution, Banks and financial institutions are under immense pressure to provide efficiency and optimize the resource. Shortage in skilled resources and increase in personnel cost and efficiency are the challenges are faced by institutions. RPA is the adoption for the institutions to overcome these challenges. RPA is a technology that uses predefined business logic, established rules and structured data to automate process. Software robots built on RPA can identify and interpret applications for Processing a transaction. Manipulating data, triggering responses, and communicating over digital systems.
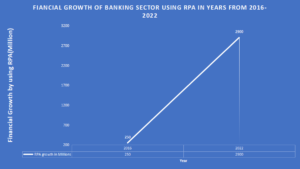
RPA is a robotic process automation software to install desktop and other end-user device-level software tools and build Artificial Intelligence workforce and virtual Assistant. RPA in finance industry used as a tool to address the demands of the banking sector and help in maximize their efficiency by reducing cost with software models. As Per McKinsey, by 2022 the Financial sector GPA increases to 2.9 Billion by 2022 compared to 2016 250 Million. Also AI in the next couple of years, where machines and software bots execute 10% to 25% of the of banking operations.
Banks has spent $321 Billion on compliance operations as well as fines. Increasing operation expense and implementing fines along with requirements to leads to lose customers and poot customer service. RPA can provide better compliance, mitigate risks, and Improve the overall customer experience by reducing manual efforts. Automation in banking sector can be possible with no additional infrastructure and low code-approach.
How RPA Works
The Goal of RPA in banking is to assist in processing repetitive tasks. RPA helps in productivity by engaging customers in real-time and leveraging the benefits of robotics. RPA is a huge process that requires robust employee training, structured inputs/instructions, and governance. RPA can take control of banking functions such as opening applications, sending emails and moving data from one application to another.
Use Cases of RPA
- Automatic Report Generation
- Customer Onboarding
- Know your customer and Anti Money Laundering
- Account Opening
- Mortgage lending
- Loan Processing
RPA Advantages
- Scalability
- Increased operational efficiency
- Cost effectiveness
- Risk and Compliance reporting
- Availability
- Zero infrastructure cost
- Faster Implementation
- Business Growth with Legacy data